Recent Post
The low-light image intensifier tubes is the core of the night vision system. It converts low light into clear images through photoelectric conversion and signal amplification. It is the "eye in the dark night" in the military, security, medical and other fields.
Precision structure: Photoelectric synergy, layers of progressive
Its core consists of photocathode (S25+ or GaAs high-sensitivity material), electron optical system, microchannel plate (MCP), phosphor screen and output window. The photocathode converts incident photons into electrons; the electron optical system focuses and accelerates electrons; the MCP amplifies the electron through cascade; electrons bombard the phosphor screen and convert them into visible light, which is presented through the output window. A high-voltage power supply ensures stable operation of the system.
Working principle: The "magic" conversion of light → electricity → light
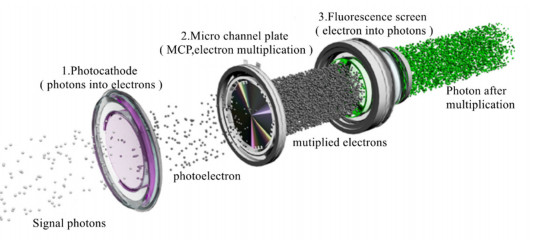
The operation process of the low-light image intensifier tubes can be summarized into three steps:
1.Photoelectric conversion: The low light from the target object is focused onto the photocathode through optical lens, and the photons stimulate electrons to escape, forming electronic image.
2.Electron multiplication: The electron flow is accelerated in the high-voltage electric field, and the secondary electron emission through the inner wall of the MCP channel is exponentially amplified, increasing the signal strength by tens of thousands of times.
3.Electro-optical conversion: High-energy electrons bombard the fluorescent screen, stimulating the phosphorescent material to emit light, and ultimately output an image with enhanced brightness, which can be observed in real time through the eyepiece or sensor.
Application scenarios: multi-field empowerment, breaking through visual limits
1.Military and Security: Used in image intensifier army night vision devices and weapon sights, enhancing nighttime reconnaissance and combat capabilities.
2.Medical and scientific research: Assisting minimally invasive surgery and clearly observing tissue details; used for astronomical observations to capture the faint light of distant stars.
3.Civil and Industrial: Provide visual support in night rescue and deep-sea exploration; integrated drones and robots to amplify night inspections and automated operations.
As a leading night vision tube manufacturer, we specialize in high-performance night vision tubes solutions, various types of image intensifier tube for sale, such as MX10160, MX11769, and MX10130.etc, suitable for PVS 31 housing, PVS 14 housing, and PVS7 night vision. We are a trusted supplier of low-light image intensifiers.